Cómo funciona el buscador de Google

Mira que he hablado de SEO Local, de Copywriting, de cómo crear contenido que posicione, del trabajo de un consultor SEO, de SEM, de Inbound Marketing e incluso de SEO en Yandex… pero… nunca os había escrito sobre lo básico en Google… así que nada, hoy solucionamos esto y sentamos las bases del posicionamiento en el buscador rey.
¡Empezamos!
La era de internet.
La llegada de internet causó un efecto revolucionario en numerosos aspectos y sin duda alguna internet marcó un antes y un después, permitiendo la entrada a la “era del conocimiento” (lo pongo entre comillas porque… mejor hablamos de eso otro día…). Cada vez son más las personas que tienen acceso a internet y, por ende, a la información que este contiene.
Pero uno no puede hablar en base solo a opiniones por eso vamos a basarnos en datos estadísticas de We Are Social y Hootsuite (tenéis los enlaces al final del artículo, en el apartado “fuentes”), que se realiza una vez al año, y donde se ha evidenciado un crecimiento acelerado de usuarios con acceso a internet, quedando demostrado que ya en 2018 el 53% de la población mundial tenía acceso a la red, mientras que en la actualidad esta cifra se ha incrementado, llegando a alcanzar los 4.660 millones de personas, lo cual representa el 59,5% de la población mundial.
En 2018 el 53% de la población mundial tenía acceso a la red, mientras que en la actualidad esta cifra se ha incrementado, llegando a alcanzar los 4.660 millones de personas, lo cual representa el 59,5% de la población mundial.
Ahora bien, de toda esta ingente cantidad de personas que acceden diariamente a internet, ya sea para entretenimiento o para realizar una búsqueda específica, la mayoría en la actualidad utilizan el buscador de Google para empezar a navegar.
Cuota de mercado de los motores de búsqueda online usados desde ordenadores de sobremesa a nivel mundial de enero de 2012 a febrero de 2021.
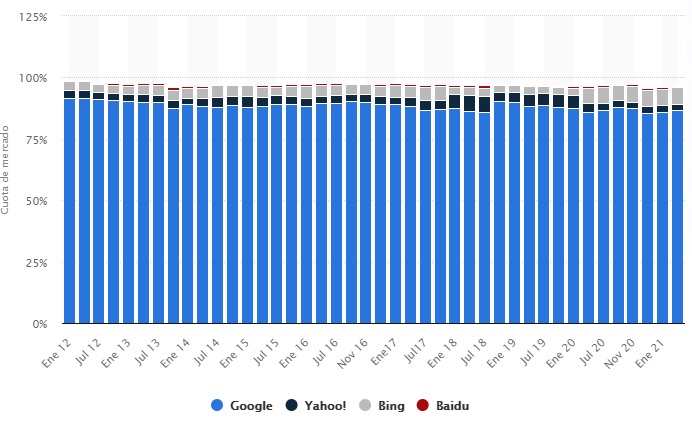
Fuente: https://es.statista.com/estadisticas/634462/cuota-de-mercado-mundial-de-los-motores-de-busqueda/
Es un hecho que existen otros buscadores, ya os he hablado de Yandex por ejemplo, el buscador ruso, pero Google tomó la delantera en los inicios y se ha consolidado como el buscador por excelencia, siendo el más rápido y preciso. Sin embargo, a pesar de que millones y millones de usuarios utilizan el buscador de Google a diario, ¿de verdad saben cómo funciona? La verdad es que nadie tiene todas las respuestas, pero hoy vamos empezar por el principio ;)
Son muchas las personas que pasan por alto este tipo de cuestionamiento, pero cada vez son más los usuarios que se preguntan cómo es posible que, dentro de la gran cantidad de información que posee la web, el buscador encuentre específicamente lo que se está buscando. Es por ello que nos tomaremos el tiempo de explicarlo de la forma más clara y sencilla a continuación.
¿Cómo funciona el buscador de Google?
Quizás lo ideal sería escuchar a Matt Cutts, uno de los mayores expertos en Google que además forma parte de la propia empresa. He traducido lo que nos dice en este vídeo para aquellos que no lleven muy bien el inglés.
Comprueba el estado de tu web o el de la competencia con esta herramienta:
Comprueba el estado de tu web o el de la competencia con esta herramienta:
Explicación de Matt Cutts de cómo funciona Google
Hola, mi nombre es Matt Cutts, soy ingeniero en el grupo de calidad de Google y hoy me gustaría hablar sobre lo que sucede cuando haces una búsqueda en la web. Lo primeroa entender es que cuando haces una búsqueda en Google no estás buscando en la web, estás buscando en el índice de la web de Google, o al menos las páginas que hemos podido encontrar.
Hacemos esto con programas de software llamados arañas. Las arañas comienzan por buscar algunas páginas web y luego siguen los enlaces en esas páginas, buscan las páginas a las que apuntan, siguen todos los enlaces en esas páginas, buscan las páginas a las que enlazan y así sucesivamente hasta que hayamos indexado una gran parte de la web. Muchos miles de millones de páginas almacenadas en miles de máquinas.
Ahora supongamos que quiero saber qué tan rápido puede correr un guepardo. Escribo mi búsqueda y pongo “guepardo”, “corriendo” y presiono Enter. Nuestro software busca en el índice para encontrar todas las páginas que incluyen esos términos de búsqueda. En caso concreto, hay cientos de miles de resultados posibles, ¿Cómo Google decide qué documentos realmente quiero ver?
Haciendo preguntas, más de 200. ¿Cuántas veces esta página contiene tus palabras clave? ¿Las palabras aparecen en el título, en la URL, directamente en el contenido? ¿la página incluye sinónimos de aquellos palabras? ¿Es esta página un sitio web de calidad o es de baja calidad? ¿incluso spam? ¿Qué es el PageRank de esta página?
Esa es una fórmula inventada por nuestros fundadores Larry Page y Sergey Brin, que califica la relevancia de una página web por el número de enlaces externos apuntan hacia ella y qué tan importantes son esos enlaces.
Finalmente combinamos todos esos factores de cada página creando la “puntuación global de la página, y te enviamos de vuelta los resultados de la búsqueda aproximadamente medio segundo después de tu búsqueda.
En Google asumimos nuestro compromiso de brindarte información útil y resultados de búsqueda imparciales, muy en serio. Nunca aceptamos pagos para agregar un sitio, actualizar su índice más a menudo, o mejorar su ranking
Echemos un vistazo en mis resultados de búsqueda. Cada entrada incluye un título, una URL y un fragmento de texto. Para ayudarme a decidir si esta página es lo que estoy buscando, también veo enlaces a páginas similares, la versión almacenada más reciente en Google de esa página y las búsquedas relacionadas que quizás deseas probar a continuación.
Y a veces a la derecha y arriba, veras anuncios.
Nos tomamos muy en serio nuestro negocio publicitario, así como nuestro compromiso de ofrecer la mejor audiencia posible a los anunciantes y nos esforzamos en mostrar solo los anuncios que realmente deseas ver.
Tenemos mucho cuidado en distinguir los anuncios de los resultados de búsqueda normales y no te mostraremos ningún anuncio si no puedes encontrar ninguno que creamos que te ayudará a encontrar la información que estás buscando, para lo cual, en este caso, la velocidad máxima de carrera de los guepardos es de más de 60 millas por hora.
Gracias por ver. Espero que esto haya hecho a Google un poco más comprensible.
Más información en https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=majWEUOmSgE
Canal JCB Digital Marketing en https://www.youtube.com/c/JavierCarmonaBenitez
Explicación de Google de cómo funciona Google
Más información en https://www.google.com/search/howsearchworks/
Resumen por fases.
Lo primero que se debe tener en cuenta es que, al momento de realizar cualquier búsqueda, el objetivo es obtener información útil que sea de ayuda, por lo que el funcionamiento del buscador se basa en indagar entre información relevante dentro de una gran base de datos, basándose en palabras claves, las cuales fueron introducidas desde el inicio, y ofrecer los resultados que mejor se ajusten a dicha búsqueda.
Para lograr lo anterior, el buscador de Google cuenta con un complejo algoritmo que la empresa ha decidido no revelar, pero que como ya hemos visto en el vídeo anterior de Matt Cutts, se nos “explica” de manera muy muy resumida el funcionamiento del buscador de Google.

En resumen, cuando ocurre una búsqueda, el buscador de Google atraviesa por tres fases importantes.
Primera fase.
1.1.- En la primera fase, entra en función un programa de software mejor conocido como “Arañas”, el cual lleva a cabo un rastreo por la base de datos, en portales que cuenten con un acceso público.
1.2.- De forma simple, las arañas se encargan de explorar un grupo de páginas con libre acceso dentro de la web, analizan su contenido y, posteriormente, siguen los enlaces que estas contienen, dirigiéndose a otras páginas similares para continuar explorando.
1.3.- Después de que el software termine de rastrear, Google proporciona toda la información recopilada para ahora indexar las miles de páginas almacenadas.
Segunda fase.
2.1.- Es entonces cuando entra en función la segunda fase de la búsqueda, la cual se encarga de almacenar la información y ordenar los datos en índices.
Por esta razón, Matt Cutts afirma que, al realizar una búsqueda en Google, en realidad no se busca por toda la web, sino dentro de los índices de búsqueda de Google. Es decir, aquellos portales que no hayan sido rastreados por las arañas y no se hayan indexado, no aparecerá en los resultados de la búsqueda.
2.2.- Ahora bien, una vez rastreados e indexados los datos, la siguiente fase consta en presentar los resultados que mejor se adapten a la búsqueda.
Existen miles de resultados, por lo que ha llegado el momento de seleccionar aquellos que sean los más adecuados. Para ello se toman en cuenta numerosos criterios, como las palabras claves, la ubicación, el idioma y la calidad y popularidad del sitio web.
El objetivo siempre será mostrar resultados imparciales que resulten útiles, por ello Google recalca que el orden de los resultados siempre será determinado por el algoritmo.
Fuentes utilizadas para redactar “Cómo funciona el buscador de Google”.
2.- Hootsuite: Informe Global Sobre el Entorno Digital 2021
3.- Descargar informe We Are Social 2021
5.- Cómo funcionan las búsquedas en Google explicado por Matt Cutts en https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=majWEUOmSgE
6.- Canal JCB Digital Marketing en https://www.youtube.com/c/JavierCarmonaBenitez











Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.